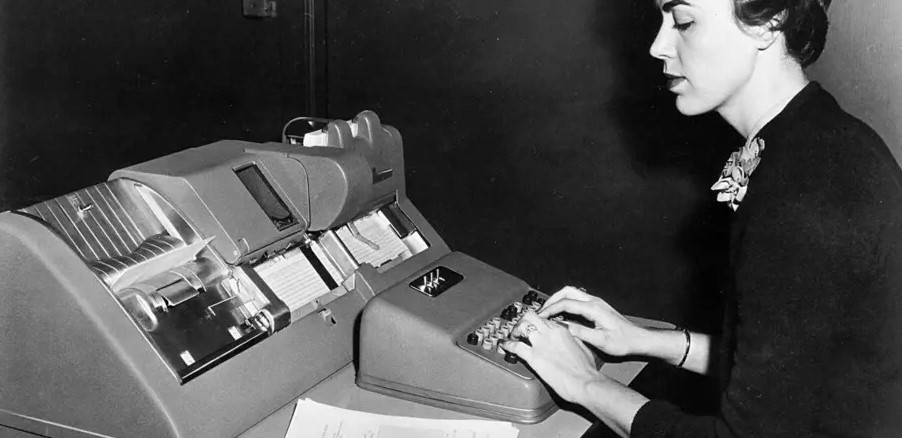

American operator punching Russian texts in IBM cards that will be put in IBM701 electronic calculator in order to be translated into English. USA, 1960s (Photo by Mondadori via Getty Images)
Translation technology is not a new vision. Over the decades it came to play an essential role the localization industry, unlocking the gateway to interconnecting cultures for global reach. Nowadays, mastering this technology is a non-negotiable for professionals seeking excellence in localization. These skills don’t just streamline the process; it fortifies a localizer’s capacity to bridge linguistic gaps more effectively, for global audiences. During Fall of 2023, my colleagues from the Middlebury Institute of International Studies at Monterey and I had the opportunity of developing some of those fundamental skills with one of the most advanced Computer-Assisted-Translation technology, (CAT tool) in the current market. This hands-on experience proved invaluable and fun to play with. It also offered the insights and lessons that I’ve compiled in this portfolio.
An interesting use of translation technology is the concept of Regular expressions, often referred to as regex.
Regex are that uses various elements and symbols to define specific criteria for matching strings. They provide a powerful and flexible way to search, manipulate, and validate strings based on specified patterns. It is a method of quality assurance that many CAT tools provide. Memorizing regex isn’t necessary either. Instead, a translator can refer to a guide with symbols and their functions. Symbols like “^” (start of line) or “\d” (any digit) form regex patterns. I’ve used Trados 2022 to apply, experiment and practice regex in a number of ways. There are a number or reasons why they important for quality and consistency in translations:
- Search and Replace: Regular expressions enable translators to perform complex search and replace operations within the text. This particularly helpful feature allows us to finding specific patterns or formatting within the text and replacing them consistently throughout the document.
- Text Cleanup: It helps to encounter parts of the documents with inconsistent formatting, punctuation, or other problems
- Quality Assurance (QA): Translators use regex to perform QA checks. They can create regex patterns to check for specific errors or inconsistencies in translations, ensuring adherence to glossaries, style guides, or formatting requirements.
- Automation: Regular expressions also facilitate automation by allowing translators to create custom rules or scripts rather creatively. These rules can automate certain translation tasks, making the process more efficient and reducing manual effort.
- Customization: Translators can create custom regular expressions to handle domain-specific terminology, specific grammar rules for a language pair, specialized formatting.
- Batch Operations: In cases where translators work with many documents or large volumes of text, regular expressions can be used to perform batch operations efficiently across all files, saving time and effort.
I’ve used Trados 2022 to apply, experiment and practice regex in a number of ways. Here are some examples of how I’ve created rules to check on some translations between English and Brazilian Portuguese:
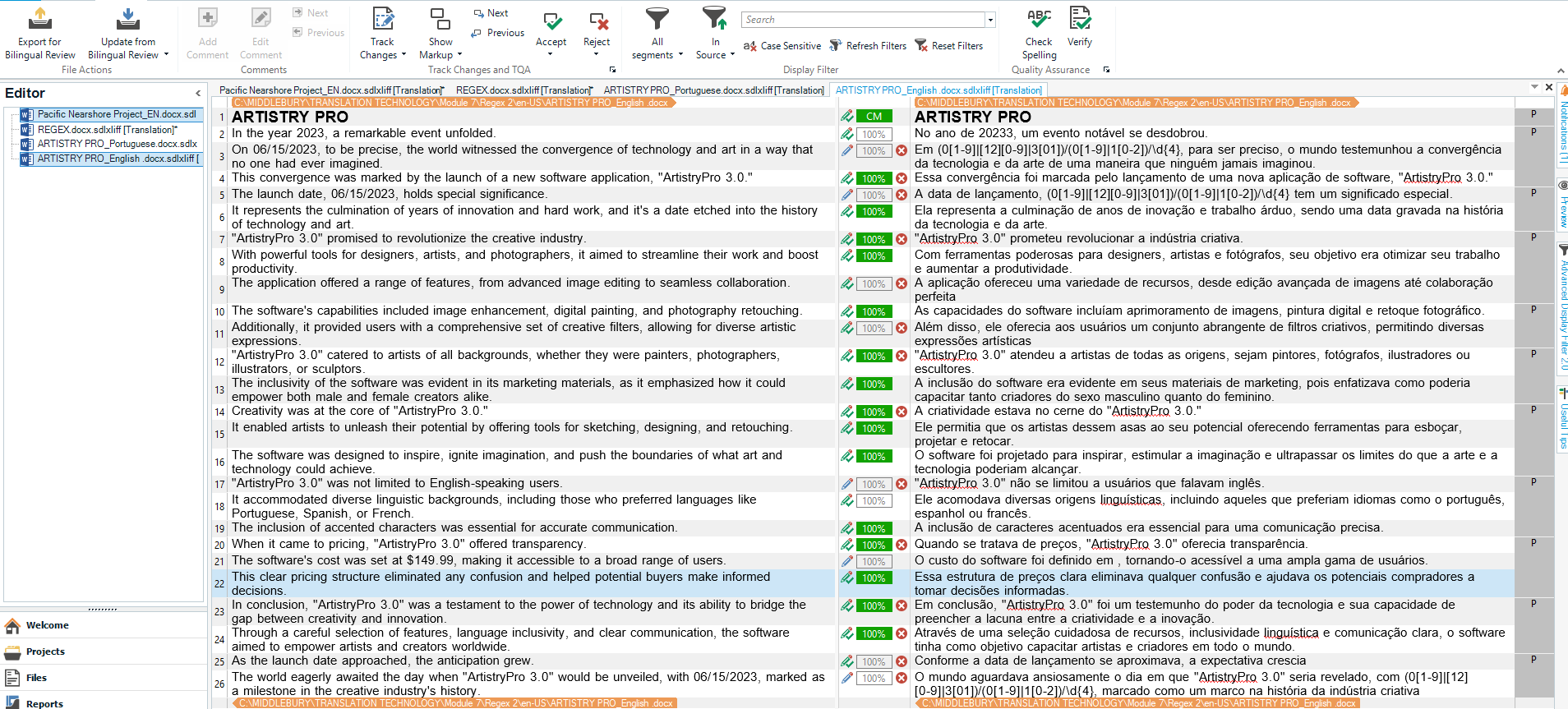
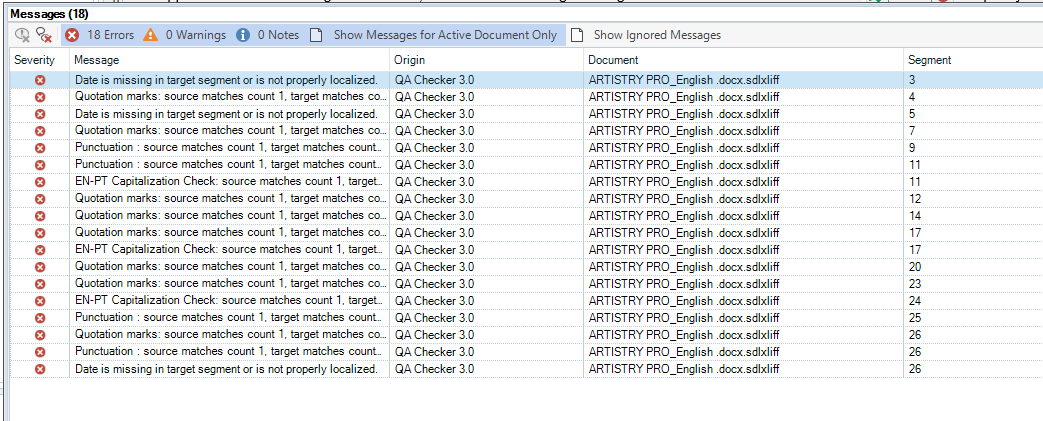
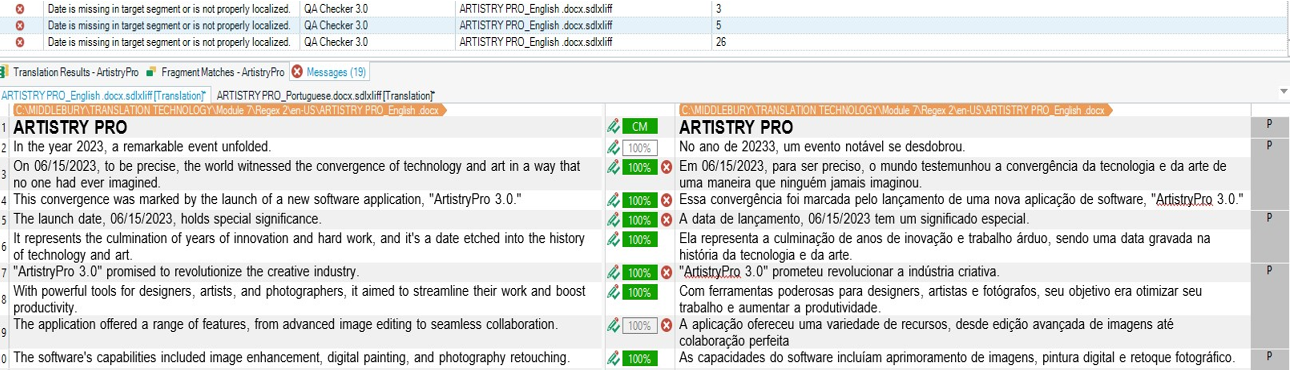
Rule 1: Date checks: \d{1,2}-\d{1,2}-\d{4}
Explanation: This rule was created to flag all date orders in the original text (EN) that appear the same in the target text (PT). This rule was created because in Portuguese the date order is different than English. Instead of MM/DD/YYYY, the order in Portuguese should be DD/MM/YYYY.
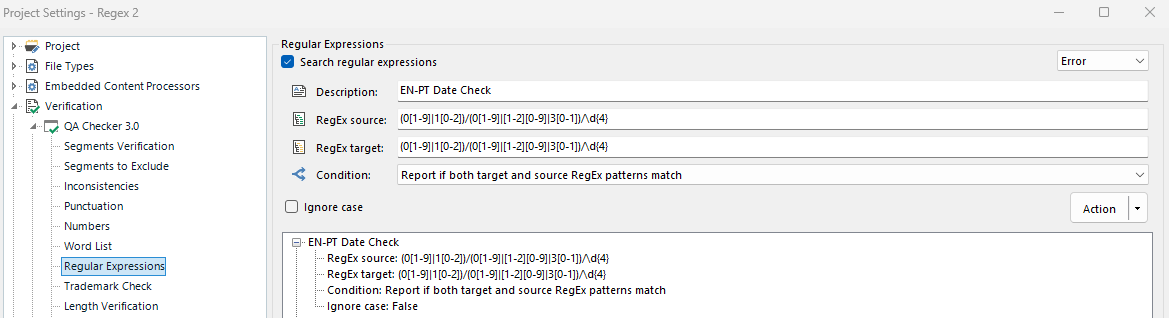
Rule 2: Quotation mark checks: “[^”]*”
Explanation: This rule was created to assure that all terms between quotation marks in English and Portuguese are the same and with no typos, since it was consistently used in this particular text.
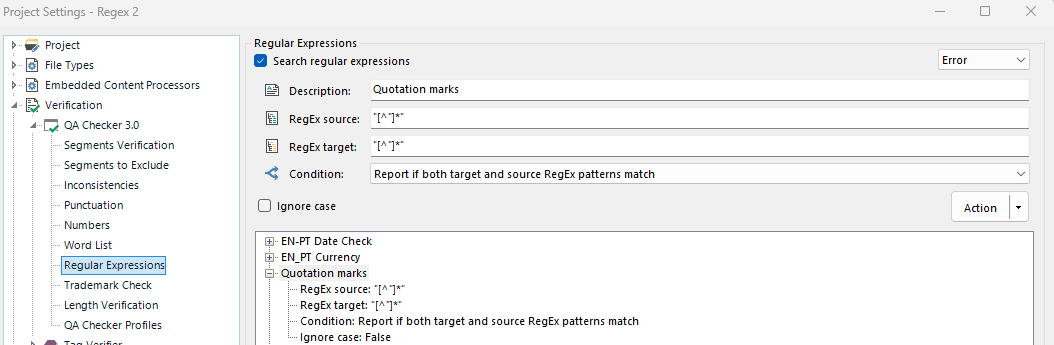
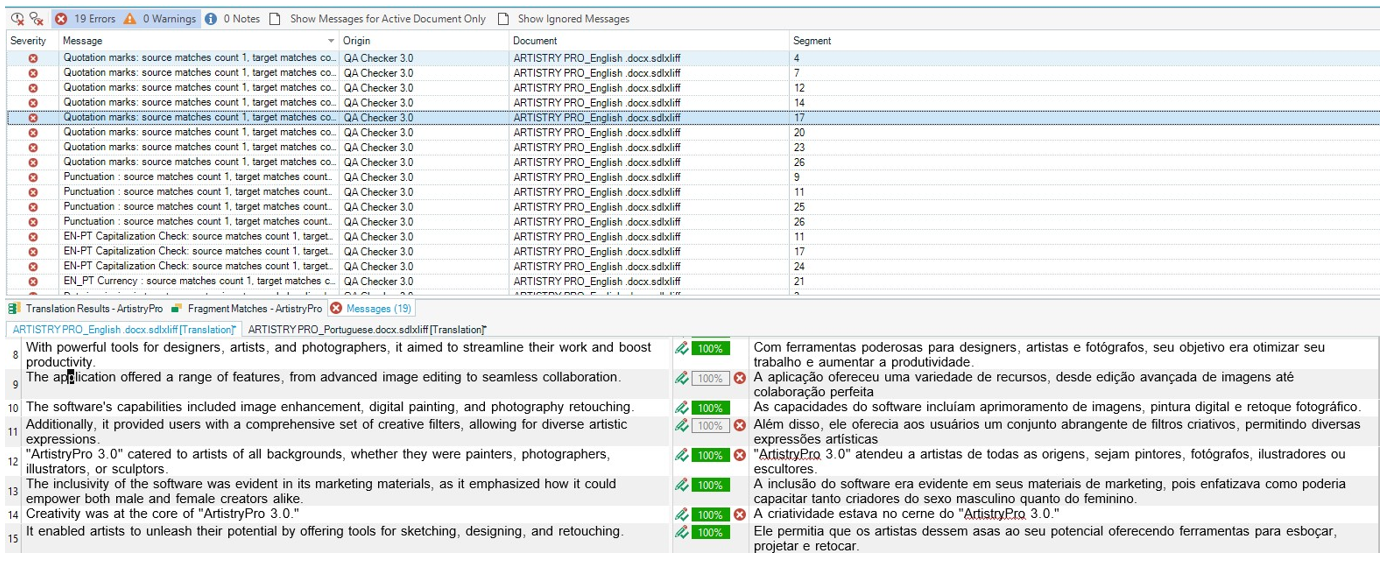
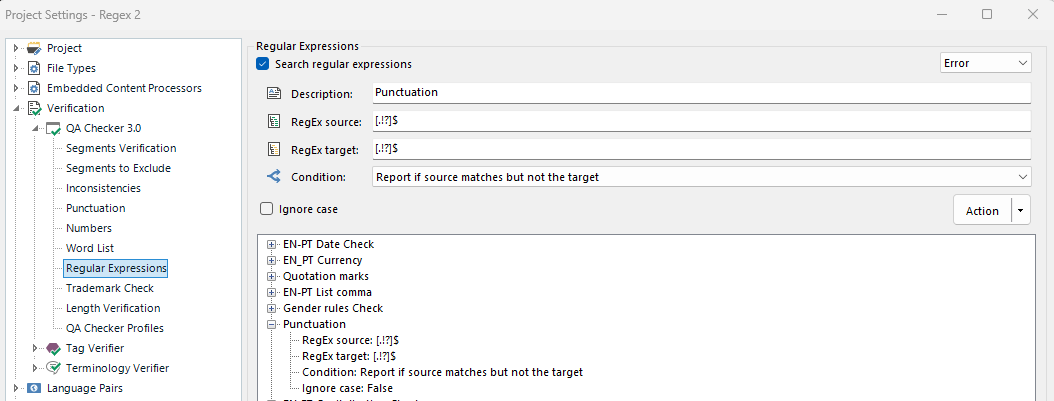
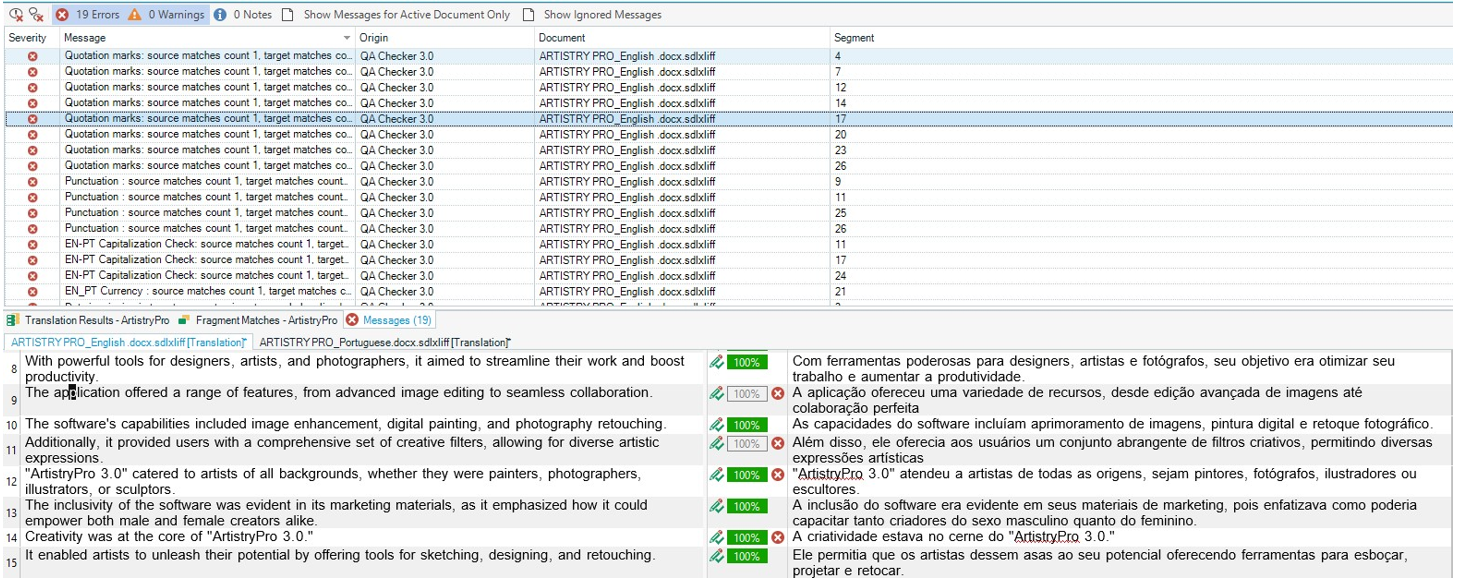
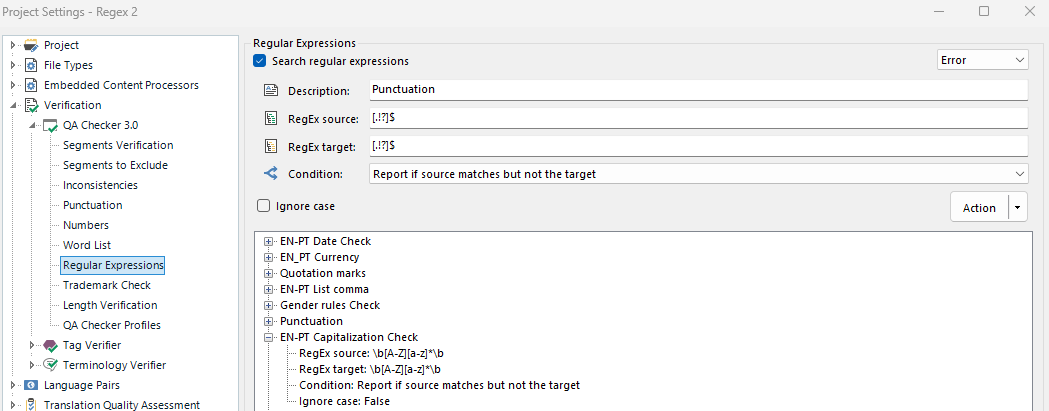
Rule 3: Punctuation: [.!?]$
Explanation: This rule was created to check for missing punctuation between the English and the Portuguese texts.
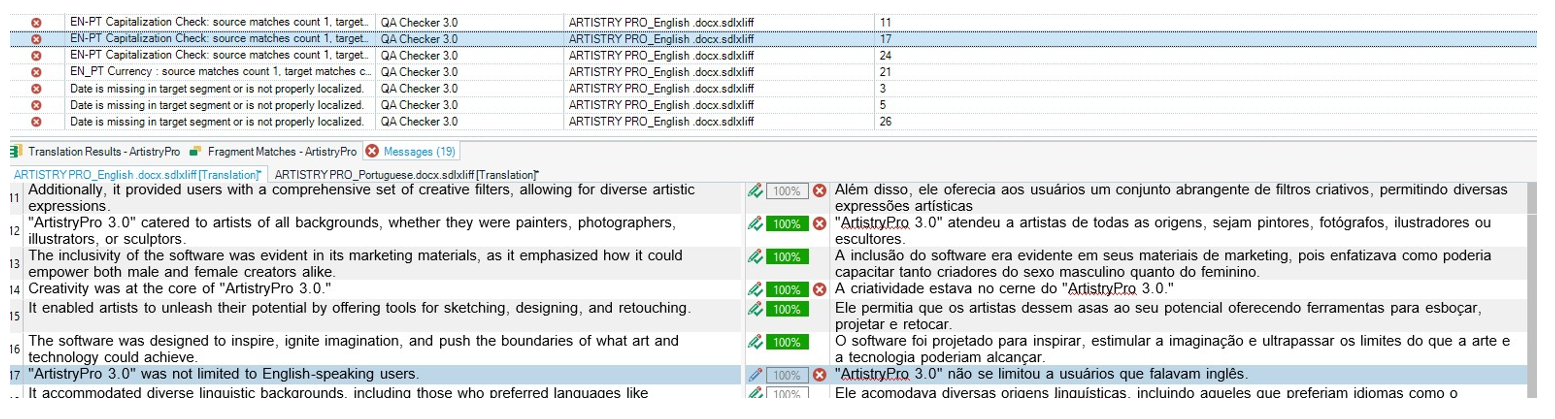
Rule 4: Capitalization check: \b[A-Z][a-z]*\b
Explanation: This rule was created to check if words that were capitalized in English were not capitalized in Portuguese. The need for this checking is multiple. Proper names in both names are capitalized but some of terms that are capitalized in English are NOT capitalized in Portuguese such as nationalities and days of the week.
Final thoughts
Regex (regular expressions) rules stand as a powerful asset for translators due to their ability to accurately manipulate text patterns. They empower translators to efficiently search, replace, and manipulate text, significantly speeding tedious tasks like finding and modifying specific phrases, formatting inconsistencies, checking on grammatical rules, and specialized terminology. This feature in CAT tools enables on-the-spot rule creation, saving time, once you can tailor rules for varied text manipulations, accordingly to the language pairs you are working on. By harnessing the precision and flexibility of regex, translators enhance productivity, ensure linguistic accuracy, and maintain consistency, therefore elevating the quality and efficiency of their translation work.
